For the most effective treatment of ACL tear in Bhubaneswar, consult Dr. Sandeep Singh. He is one of the best orthopedic doctors in Bhubaneswar. Consult at 8658044823
Anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear is one of the most prevalent knee injuries. Athletes that engage in high-demand sports such as football, soccer, and basketball are more likely to get anterior cruciate ligament injuries.
ACL reconstruction is a procedure that involves using an arthroscope and creating small incisions to restore the anterior cruciate ligament. Arthroscopic surgery is less intrusive than conventional surgery. Less invasive techniques have the advantages of less pain from surgery, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery.
Dr. Sandeep Singh, one of the best orthopedic doctors in Bhubaneswar, is well known for his expertise in ACL repair surgery. He is a sports injury and joint replacement specialist with a wealth of experience. Years of expertise have enabled him to amass a wealth of technical proficiency in ACL reconstruction.
So, without a doubt, you should consult Dr. Sandeep Singh for treating ACL injury in Bhubaneswar.
Now, let’s talk about the causes of an ACL tear, its symptoms, and when to seek medical help.
What Causes Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear?
- ACL injuries are common in athletes who stop and change directions abruptly while running.
- People who compete in sports like soccer, football, tennis, basketball, volleyball, or gymnastics are more prone to twist their knees by accident than, say, cross-country runners who race at a steady pace.
- Your pace, combined with how you twist or turn your knee, increases your chances of stretching or tearing your ACL.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear?

- Pain. You may not experience pain if you have a mild injury. You may experience pain along the joint line of your knee. Some patients find it difficult to stand or apply pressure to the injured limb.
- Swelling. During the first 24 hours, this is most likely to happen. Applying ice to your knee and elevating (lifting) your leg with a pillow will help minimize swelling.
- Difficulty walking. If you put pressure on your injured leg, you may realize that walking is more difficult than usual. The knee joint may feel looser than it should for certain people.
- Reduction in range of motion. After you have torn your ACL, you won’t be able to bend and flex your knee as much as you used to.
How is ACL Tear Diagnosed?
Dr. Sandeep Singh, one of the best ortho doctors in Bhubaneswar, may need to know the specifics of the patient’s knee injury. He will examine both knees to discover if the one that’s bothering the patient appears different. Dr. Singh may perform or recommend the following diagnostics:
- Physical examination. The doctor may instruct the patient to lie down on the back and bend the hips and/or knees at different angles.
Next, the doctor will gently shift the patient around by placing the hands-on various areas of the leg.
If any of the patient’s bones move abnormally, it could signify that the ACL has been damaged.
- X-ray. Although X-rays don’t show soft tissues like the ACL, the doctor may want to rule out fractured bones.
- Ultrasound or MRI. Both soft tissue and bone can be seen during these examinations. If the ACL is destroyed, it should show up in the images.
- Arthroscopy. This means “to see within the joint.” Dr. Sandeep Singh, one of the best orthopedists in Bhubaneswar, will create a small cut in the patient’s skin during arthroscopy.
What is the Treatment for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear?
The treatment depends on the severity of the ACL injury. Here are some of the alternatives your doctor may give you:
- First aid. If your damage is minimal, all you need to do is apply ice to your knee, elevate your leg, and take some time off your feet. Wrapping an ace bandage across your knee will help minimize swelling. Crutches might assist in reducing weight from your knee.
- Medications. Anti-inflammatory medications can aid in the alleviation of swelling and pain. Your doctor may advise you to take over-the-counter drugs or prescribe a stronger medication. Your doctor may inject steroid medication into your knee if you are in a lot of discomfort.
- Knee brace. Some patients with a torn ACL can benefit from wearing a brace on their knee when running or participating in sports. It provides further assistance.
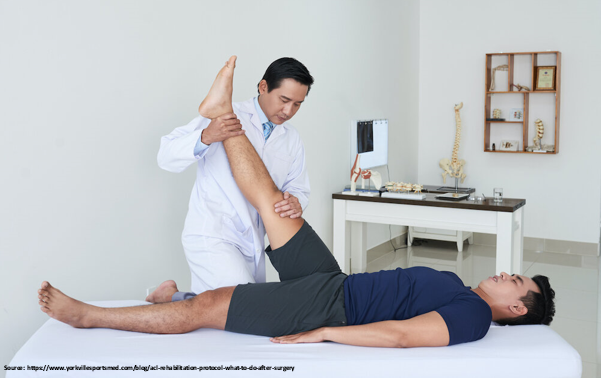
- Physiotherapy. To get your knee back in action, you may need to do this a few times a week. You should do exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee and restore a complete range of motion during your sessions. You may be sent home with activities to complete on your own.
- Surgery. If your ACL is severely torn, if your knee gives way when walking, or if you are an athlete, your doctor may recommend surgery.
The surgeon will remove the injured ACL and replace it with tissue to allow a new ligament to develop in its place. People who have had surgery can typically return to sports within a year with the help of physical therapy.
Whether surgery is used in your treatment or not, rehabilitation is critical to bringing you back to your normal routine. You might be able to restore knee function and motion with the help of physiotherapy.
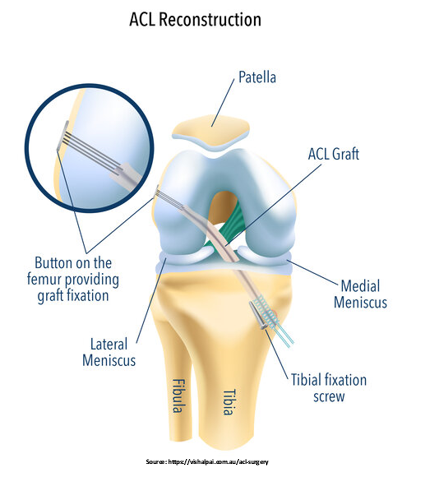
If you have had surgery, physiotherapy will focus on restoring motion to the joint and surrounding muscles. Following that, a strengthening regimen to protect the new ligament should be implemented. The stress across the ligament gradually increases as the ligament is strengthened. The athlete’s sport-specific functional return is the goal of the final rehabilitation phase.